PCB Equipment Overview: Facts, Details, and Modern Innovations
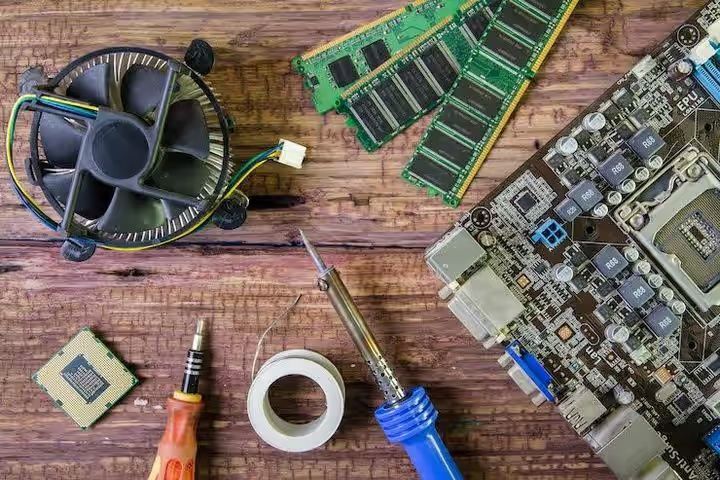
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the foundation of nearly every modern electronic device, from smartphones and computers to medical instruments and electric vehicles. PCB equipment refers to the specialized machinery used in the design, manufacturing, testing, and assembly of these circuit boards.
The primary goal of PCB equipment is to automate and streamline production, ensuring precision and reliability. These machines handle multiple processes such as:
-
Etching and drilling to create pathways for electrical signals.
-
Component placement using automated pick-and-place machines.
-
Soldering and inspection for quality assurance.
Over the decades, PCB manufacturing has evolved from manual assembly to advanced automation involving robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and computer-aided design (CAD). This shift has enabled higher production volumes, reduced errors, and supported increasingly compact and complex electronic designs.
Importance – Why PCB Equipment Matters Today
In today’s digital and connected world, PCB equipment plays a critical role in global innovation. Every device that relies on electronic control depends on reliable PCB fabrication and assembly.
Key Reasons PCB Equipment Is Essential
-
Backbone of Modern Electronics: From consumer gadgets to aerospace systems, PCBs form the central nervous system of electronic circuits.
-
Precision and Reliability: Advanced machines ensure high accuracy, preventing costly defects and enhancing product longevity.
-
Miniaturization and Efficiency: New-generation PCB equipment supports smaller designs with higher functionality, enabling the rise of wearables and IoT devices.
-
Sustainability Goals: Energy-efficient machines and eco-friendly materials are helping manufacturers reduce waste and environmental impact.
-
Economic Significance: PCB production supports multiple industries including telecommunications, automotive, healthcare, and renewable energy.
For engineers, manufacturers, and policymakers, PCB equipment determines how efficiently technology can advance while maintaining affordability and sustainability.
Recent Updates – Innovations and Industry Trends (2024–2025)
The PCB industry is witnessing transformative innovations driven by automation, sustainability, and high-speed computing.
| Trend | Description | Impact (2024–2025) |
|---|---|---|
| AI-Driven Manufacturing | Artificial intelligence enhances defect detection, predictive maintenance, and design optimization. | Improved accuracy and reduced downtime |
| Flexible and Rigid-Flex PCBs | Increasing demand for foldable and wearable devices is fueling innovations in flexible circuit manufacturing. | Expected global growth by 15% by 2025 |
| 5G and High-Frequency PCBs | Equipment upgrades support the production of high-frequency boards for faster data communication. | Critical for telecom and IoT sectors |
| Laser Drilling Technology | Replacing mechanical drilling for precision microvias in multilayer PCBs. | Faster production with higher accuracy |
| Sustainability and Recycling | Manufacturers adopting lead-free soldering and recyclable substrates to reduce waste. | Aligns with global green manufacturing goals |
Market Insights
According to 2024 reports from industry analysts, global PCB equipment demand has risen sharply due to electric vehicle (EV) and renewable energy industries. Automation and robotics integration in PCB assembly are projected to reduce human error rates by up to 30% by 2025.
Laws or Policies – Regulations Affecting PCB Manufacturing
Governments worldwide have introduced rules to ensure that PCB production is environmentally responsible and safe for workers.
1. Environmental and Safety Regulations
-
RoHS Directive (Restriction of Hazardous Substances – EU): Limits the use of toxic materials such as lead, mercury, and cadmium in PCBs.
-
REACH Regulation (EU): Ensures safe use of chemicals in electronics production.
-
WEEE Directive (EU): Promotes the recycling of electronic waste, encouraging manufacturers to design PCBs for easy disassembly.
2. Industry Standards
-
IPC Standards (Global): Issued by the Association Connecting Electronics Industries, covering quality, design, and manufacturing guidelines (e.g., IPC-A-600 for PCB acceptability).
-
ISO 9001 & ISO 14001: Ensure quality management and environmental responsibility in PCB manufacturing.
3. National Policies and Initiatives
-
India: Under the “Make in India” initiative, PCB and semiconductor manufacturing are prioritized through tax incentives and import duty reductions.
-
United States: The CHIPS and Science Act (2022) continues to boost domestic PCB and semiconductor supply chain resilience.
-
China: Focuses on automation and green manufacturing through subsidies and R&D funding for smart PCB equipment.
These regulations and incentives encourage cleaner, safer, and more efficient PCB production across the globe.
Tools and Resources – Modern Equipment and Software for PCB Production
PCB design and manufacturing rely on specialized tools, both hardware and software, to achieve precision and efficiency.
Common PCB Equipment Types
| Equipment Type | Function | Example Use |
|---|---|---|
| CNC Drilling Machines | Create precise holes for components and vias | Multilayer PCB manufacturing |
| Pick-and-Place Machines | Automatically place components on PCBs | High-speed assembly lines |
| Soldering Machines | Ensure strong connections between components and board | Wave soldering or reflow soldering |
| AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) | Detect defects using high-resolution cameras | Quality control and testing |
| Lamination Presses | Bond multiple layers under heat and pressure | Used in multilayer PCB fabrication |
Essential PCB Software Tools
| Software | Purpose | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Altium Designer | PCB layout and design | Used by engineers for schematic capture and simulation |
| KiCad | Open-source PCB design software | Ideal for educational and small-scale projects |
| EAGLE | Design and routing | Integrates with Autodesk for prototyping |
| OrCAD | Circuit simulation and analysis | Preferred for advanced electronic system design |
Online Resources and Calculators
-
PCBWay and JLCPCB: Offer online fabrication cost estimators and design-to-production tools.
-
Saturn PCB Toolkit: Helps calculate impedance, current capacity, and thermal performance.
-
PCB Prototype Calculator: Determines board thickness, copper weight, and trace width.
These tools simplify PCB design and production, helping professionals balance performance, cost, and compliance.
Example Table: PCB Manufacturing Process Overview
| Stage | Description | Equipment Used |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Electrical layout planning and simulation | PCB design software (Altium, KiCad) |
| Fabrication | Etching, drilling, and plating to form circuit layers | CNC machines, laser drills |
| Assembly | Mounting and soldering components | Pick-and-place, reflow ovens |
| Testing | Inspection for electrical or physical defects | AOI, X-ray inspection, ICT |
| Packaging | Final product protection and delivery | Cleaning and packaging systems |
FAQs – Common Questions About PCB Equipment
1. What does PCB equipment do?
PCB equipment handles every stage of circuit board production, including drilling, etching, component placement, and inspection to ensure reliability and performance.
2. What are the main types of PCBs produced today?
The most common types include single-layer, double-layer, multilayer, flexible, and rigid-flex PCBs, depending on their use in different electronic devices.
3. How is automation changing PCB manufacturing?
Automation and robotics reduce errors, improve production speed, and enable real-time quality control, making PCB production more efficient and scalable.
4. What is the difference between traditional and flexible PCBs?
Traditional PCBs are rigid and used in standard electronics, while flexible PCBs are bendable and suitable for compact or wearable devices.
5. How are environmental concerns being addressed in PCB production?
Manufacturers now use lead-free solder, recyclable substrates, and energy-efficient machinery to minimize environmental impact, aligning with RoHS and ISO standards.
Conclusion
PCB equipment forms the foundation of modern electronics manufacturing, driving the global shift toward automation, sustainability, and high-performance design. With advancements like AI-driven inspection and flexible PCB production, the industry is entering an era of smarter, greener, and more efficient manufacturing. Understanding the equipment, tools, and regulations behind PCB production helps engineers, manufacturers, and policymakers ensure that the future of technology remains both innovative and responsible.